There are several blood pressure medications available on prescription; in fact, an overwhelming array for people to choose from. If you want to lower your blood pressure, and are unsure which medicine to select, here’s a helpful guide, outlining some of the most common types of medication and their side effects.
Blood Pressure Medication and Side Effects
- Atenolol. Atenolol is a beta blocker; which acts to block certain chemicals within the body, lowering heart rate and blood pressure. The most common side-effects associated with this drug are light-headedness, fatigue and nausea. Severe symptoms are rare, but can include fainting, depression and even heart failure.
- Lisinopril. Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor, and targets blood vessels, causing them to relax so that blood can flow more easily. However, it’s not without its side-effects. Common complaints include headache or dizziness, though this generally disappears after a short period of time. More serious side-effects can include: fainting, irregular heart-beat, severe stomach pain and even liver problems.
- Nebivolol. Nebivolol is a commonly used beta-blocker. Occasionally, users of this medication may experience nausea, headache, slower heartbeat and insomnia. It’s unlikely you’ll encounter any severe side-effects, but there have been rare cases where users have experienced worsening asthma, and symptoms of heart failure.
- Valsartan. Also used to protect from kidney damage, Valsartan is an ARB, or angiotensin receptor blocker. This works by helping the blood vessels to relax, enabling blood to flow more easily. The most important thing to be aware of with Valsartan is that it can cause serious harm to unborn babies, and can even result in fetal death. In addition to this, it’s fairly common to experience mild dizziness whilst your body becomes acclimatized to the drug.
- Hydrochlorothiazide. Hydrochlorothiazide, more commonly known as Microzide, acts as a diuretic, helping the body to flush through salt more efficiently and reduce the risk of heart disease. The most serious risk associated with this medication is dehydration, and it’s important to drink enough fluids when taking it. You may also experience upset stomach and dizziness, though this should only be temporary.
More Questions? Speak to a Cardiovascular Specialist
If you’re about to start taking new medication, it’s important that you know about the side-effects, as well as the benefits. Ask your doctor or cardiovascular specialist, and make sure you make an informed decision when it comes to your health.
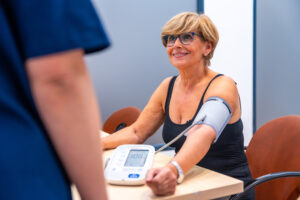 Daily schedules rarely slow down. A buzzing phone, a stalled commute, or a tense meeting can each jolt the body into high alert for a moment. Stack enough of those moments together, and blood‑pressure readings begin to drift upward in ways that will not fade once traffic clears. Read More
Daily schedules rarely slow down. A buzzing phone, a stalled commute, or a tense meeting can each jolt the body into high alert for a moment. Stack enough of those moments together, and blood‑pressure readings begin to drift upward in ways that will not fade once traffic clears. Read More 

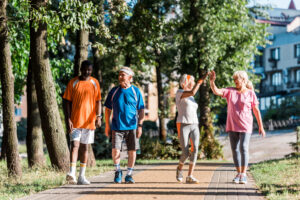 If you’ve been diagnosed with high blood pressure, also known as
If you’ve been diagnosed with high blood pressure, also known as  When most people think of high blood pressure, they often associate it with middle-aged or older adults. However,
When most people think of high blood pressure, they often associate it with middle-aged or older adults. However, 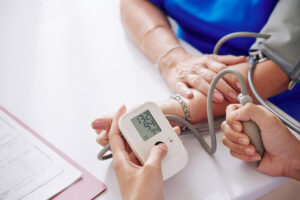 High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it can go unnoticed until significant damage has been done to vital organs. While lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress management play a pivotal role in managing blood pressure, genetics also play a significant part in determining individual risk. Understanding this connection can help individuals take proactive steps to safeguard their health.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it can go unnoticed until significant damage has been done to vital organs. While lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress management play a pivotal role in managing blood pressure, genetics also play a significant part in determining individual risk. Understanding this connection can help individuals take proactive steps to safeguard their health.
